Unlocking the Brain’s Potential : Exploring adult neurogenesis and it’s potential in cognitive well being
Updated on: April 10, 2024
Exploring adult neurogenesis and it’s potential in cognitive well being
Understanding the Adult Neurogenesis:
Adult neurogenesis, the process of generation and integration of new neurons in the adult brain, has emerged as a topic of fascination and scientific query in past few decades. It challenges the long held belief that brain has a limited capacity of regeneration. Once believed preposterous, research over the past few decades has unravel the remarkable ability of adult brain to produce new neurons throughout the life. Since its discovery, adult neurogenesis has sparked significant interest in understanding its implications for cognitive function, mental health, and aging.
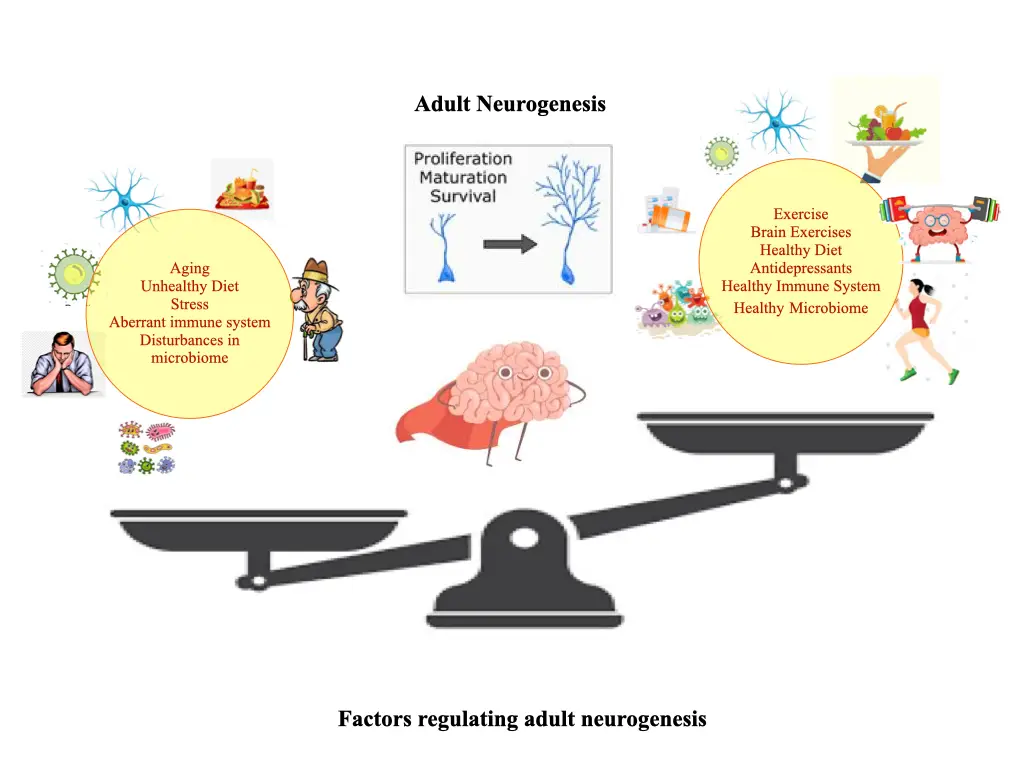
Adult neurogenesis primarily occurs in two distinct brain regions of the brain : The dentate gyrus (DG) region of hippocampus, which is actively involved in learning and memory and sub ventricular zone (these newly born neurons later migrates to forebrain regions mainly to the olfactory bulb and get incorporated into the olfactory neural circuitry). Neural stem cells residing in these two regions give rise to the new neurons via a stepwise complex process involving proliferation , differentiation , migration and integration into pre-existing neural circuitry.
There are various factors which directly or indirectly regulate the process of neurogenesis at any of these stages. For example , voluntary exercises , healthy diet, antidepressants etc. have been reported to stimulate the process of adult neurogenesis. Moreover, some recent findings have also reported the role of gut microbiota in the maintenance of brain-immune system coherence and modulation of adult neurogenesis. On the other hand , factors such as stress, unhealthy diet, and sedentary lifestyles are some of the negative modulators of adult neurogenesis.
The Concept of use it or lose it:
The phrase "use it or lose it" aptly captures the essence of how engagement in stimulating activities may influence adult neurogenesis and subsequently impact brain health. The discovery of adult neurogenesis challenges the traditional view of brain as a static organ with fixed neuronal populations. Instead , it highlights the remarkable capacity of our brain to regenerate and adapt as per new experiences throughout the life. Adult neurogenesis is believed to play a pivotal role in cognitive functioning and mood regulations. Exposure to enriched environment along with increased sensory, cognitive and social stimulation promotes adult neurogenesis. Environment enrichment enhances synaptic plasticity and improve cognitive resilience against age-associated decline.
Physical activity or exercise has emerged as an another potent modulator of adult neurogenesis exerting beneficial effects on brain structure and its functionality. Aerobic exercise enhances neurotrophic factors, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which promotes neuronal growth, survival, and synaptic plasticity. Further, it is associated with improved cognitive performance, reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases, and enhanced mood, underscoring the importance of an active lifestyle in maintaining brain health. Learning and cognitive stimulation have been linked to increased neurogenesis and neuronal integration in the adult brain.
TIt is worth noting that activities which challenge the brain, such as learning a new language, playing musical instruments, or engaging in complex problem solving tasks, can promote the formation of new neural connections and enhance cognitive function. Social isolation and chronic stress have been shown to negatively impact adult neurogenesis, contributing to cognitive deficits and mood disorders. In contrast, social engagement and positive social interactions can enhance neurogenesis, promote stress resilience, and improve emotional well-being. Maintaining strong social connections and participating in meaningful social activities are crucial for supporting brain health and neurogenesis throughout adulthood.
Harnessing the Potential of Brain’s Neurogenic Abilities:
Neurogenic ability of adult brain may significantly contribute to brain repair and recovery following a traumatic injury or disease.While the exact mechanism of adult neurogenesis regulation is still being elucidated, factors such as environmental enrichment , physical exercise, social interaction and learning have been shown to enhance the process. Lifelong learning not only stimulates neurogenesis but also fosters cognitive reserve, providing a buffer against age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. The emerging evidence on adult neurogenesis underscores the dynamic nature of the adult brain and its capacity for regeneration and adaptation.
The concept of "use it or lose it" encapsulates the idea that engaging in enriching activities, such as environmental stimulation, physical exercise, cognitive challenges, and social interaction, can promote the survival and integration of newly generated neurons, thereby preserving brain function and resilience against age-related decline and neurodegenerative diseases. Embracing a lifestyle that nurtures adult neurogenesis holds profound implications for promoting lifelong brain health and well-being.
Understanding the process of adult neurogenesis regulation holds significant implications for brain health and treatment of neurological disorders. Scientific evidences suggest that neurogenesis promotion through lifestyle interventions such as cognitive stimulation and a healthy diet could enhance cognitive well-being and prevent against age associated cognitive decline. In addition , harnessing the regenerative potential of adult brain may offer new avenues for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Conclusion
Adult neurogenesis represents a fascinating phenomenon which highlights the brain’s ability for regeneration and adaptability. Active lifestyle and dietary modifications may potentiate our brain neurogenic abilities and thus may slow down the age associated neurodegeneration. By unraveling the mysteries of adult neurogenesis scientists are not only expanding our understanding of brain function but also paving new path for novel therapeutic approaches to neurological disorders.
Written By :
Dr Shweta Tripathi
Assistant Professor
Paramedical Sciences (Neurosciences and Neurotechnology)
School of Allied Health Sciences,
SGT University , Budhera, Gurugram

